Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
3D Visualization with PyVista#
The example demonstrates the how to use the VTK interface via the pyvista library . To run this example, you will need to install pyvista .
contributed by @banesullivan
Using the inversion result from the example notebook plot_laguna_del_maule_inversion.ipynb
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
import discretize
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
import pooch
# Set a documentation friendly plotting theme
pv.set_plot_theme("document")
print("PyVista Version: {}".format(pv.__version__))
PyVista Version: 0.46.4
Download and load data#
In the following we load the mesh and Lpout that you would
get from running the laguna-del-maule inversion notebook as well as some of
the raw data for the topography surface and gravity observations.
# Download Topography and Observed gravity data
data_url = "https://storage.googleapis.com/simpeg/Chile_GRAV_4_Miller/Chile_GRAV_4_Miller.tar.gz"
downloaded_items = pooch.retrieve(
data_url,
known_hash="28022bf8802eeb4892cac6c3efd1eb4275c84003a6723c047fe5e1738a66ea04",
processor=pooch.Untar(),
)
data_path = next(filter(lambda f: f.endswith("LdM_grav_obs.grv"), downloaded_items))
topo_path = next(filter(lambda f: f.endswith("LdM_topo.topo"), downloaded_items))
model_url = "https://storage.googleapis.com/simpeg/laguna_del_maule_slicer.tar.gz"
downloaded_items = pooch.retrieve(
model_url,
known_hash="107293bfdeb77b314f4cb451a24c2c93a55aae40da28f43cf3c075d71acfb957",
processor=pooch.Untar(),
)
mesh_path = next(filter(lambda f: f.endswith("mesh.json"), downloaded_items))
model_path = next(filter(lambda f: f.endswith("Lpout.npy"), downloaded_items))
# # Load the mesh/data
mesh = discretize.load_mesh(mesh_path)
models = {"Lpout": np.load(model_path)}
Downloading data from 'https://storage.googleapis.com/simpeg/Chile_GRAV_4_Miller/Chile_GRAV_4_Miller.tar.gz' to file '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/1aa04a54c5738d4bb795040e61b8adaa-Chile_GRAV_4_Miller.tar.gz'.
Untarring contents of '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/1aa04a54c5738d4bb795040e61b8adaa-Chile_GRAV_4_Miller.tar.gz' to '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/1aa04a54c5738d4bb795040e61b8adaa-Chile_GRAV_4_Miller.tar.gz.untar'
Downloading data from 'https://storage.googleapis.com/simpeg/laguna_del_maule_slicer.tar.gz' to file '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/5f2aebc57c6e4821887113b9d5c65f53-laguna_del_maule_slicer.tar.gz'.
Untarring contents of '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/5f2aebc57c6e4821887113b9d5c65f53-laguna_del_maule_slicer.tar.gz' to '/home/vsts/.cache/pooch/5f2aebc57c6e4821887113b9d5c65f53-laguna_del_maule_slicer.tar.gz.untar'
Create PyVista data objects#
Here we start making PyVista data objects of all the spatially referenced data.
# Get the PyVista dataset of the inverted model
dataset = mesh.to_vtk(models)
dataset.set_active_scalars("Lpout")
(<FieldAssociation.CELL: 1>, pyvista_ndarray([0.02552159, 0.02554211, 0.02568049, ..., nan,
nan, nan], shape=(190440,)))
# Load topography points from text file as XYZ numpy array
topo_pts = np.loadtxt(topo_path, skiprows=1)
# Create the topography points and apply an elevation filter
topo = pv.PolyData(topo_pts).delaunay_2d().elevation()
# Load the gravity data from text file as XYZ+attributes numpy array
grav_data = np.loadtxt(data_path, skiprows=1)
print("gravity file shape: ", grav_data.shape)
# Use the points to create PolyData
grav = pv.PolyData(grav_data[:, 0:3])
# Add the data arrays
grav.point_data["comp-1"] = grav_data[:, 3]
grav.point_data["comp-2"] = grav_data[:, 4]
grav.set_active_scalars("comp-1")
gravity file shape: (191, 5)
(<FieldAssociation.POINT: 0>, pyvista_ndarray([-1.15534e+01, -1.44465e+01, -5.33190e+00, -1.63014e+01,
-1.30721e+01, -1.39600e-01, 5.68720e+00, -7.10900e-01,
4.71980e+00, 1.23900e+00, 3.68730e+00, -5.31380e+00,
4.14140e+00, -3.58090e+00, 3.94350e+00, 4.07840e+00,
-1.14430e+00, 3.99480e+00, 5.58800e-01, -1.40378e+01,
-1.43858e+01, -1.63174e+01, -1.16554e+01, -2.87140e+00,
-9.56420e+00, -2.25410e+00, -4.58700e-01, -5.24410e+00,
4.90410e+00, 5.52340e+00, 3.87690e+00, 4.02540e+00,
3.81050e+00, 2.83610e+00, 2.56460e+00, -1.63680e+00,
-4.29360e+00, -5.44530e+00, -3.38050e+00, -3.28940e+00,
-1.83590e+00, -8.48700e-01, -1.09720e+00, -1.92030e+00,
-8.58400e-01, 9.17100e-01, 2.08710e+00, 3.63410e+00,
3.87850e+00, 4.20830e+00, 3.76590e+00, 4.37010e+00,
4.97830e+00, 5.47840e+00, 4.20080e+00, 4.53510e+00,
3.87420e+00, 3.80150e+00, 3.70450e+00, 4.18960e+00,
4.14460e+00, 3.69240e+00, 2.99500e+00, 2.57130e+00,
2.82980e+00, 4.18930e+00, 2.37200e+00, 2.24040e+00,
-1.57320e+00, -2.95570e+00, -6.11860e+00, -8.62850e+00,
4.23130e+00, 3.87100e+00, 4.25970e+00, 3.98770e+00,
3.07480e+00, 2.33480e+00, -1.16109e+01, -9.84730e+00,
-5.55460e+00, -9.33400e-01, -7.04800e-01, -2.49900e-01,
-1.01720e+00, 1.10040e+00, 7.12600e-01, 5.52700e-02,
-4.48000e-02, -6.12000e-01, -2.54110e+00, -5.06770e+00,
-1.33736e+01, 4.70080e+00, 2.96350e+00, 1.79560e+00,
1.23870e+00, 4.76700e-01, 3.94200e-01, 4.63400e-01,
1.67910e+00, -2.09600e-01, -1.03530e+00, -2.36800e-01,
-3.75900e-01, 1.89900e+00, 3.70720e+00, 5.07700e+00,
6.06070e+00, 4.37360e+00, 4.37840e+00, 2.24920e+00,
2.81660e+00, 5.34190e+00, 5.86920e+00, 4.18790e+00,
3.95290e+00, 8.15200e-01, -1.27156e+01, -1.43970e+01,
-1.74116e+01, -1.86309e+01, -1.81361e+01, 4.94820e+00,
3.93680e+00, 1.32440e+00, -3.41200e-01, 1.65010e+00,
-1.22760e+00, -1.81560e+00, -3.28520e+00, -3.09490e+00,
-4.19520e+00, -3.48290e+00, -3.78440e+00, -3.26540e+00,
-3.08930e+00, -3.90630e+00, -4.93810e+00, -7.21930e+00,
-5.10450e+00, -9.73700e-01, -9.08700e-01, 2.24600e-01,
-8.98800e-01, -4.72800e-01, -1.19300e-01, -1.83000e-02,
-1.00700e+00, -8.17600e-01, -1.45390e+00, -1.59900e-01,
-8.91000e-02, -1.34800e+00, 5.03900e-01, -6.82900e-01,
-1.38463e+01, -1.56983e+01, -1.27892e+01, -1.24353e+01,
5.16970e+00, 7.08610e+00, 8.82880e+00, 9.56390e+00,
9.91700e+00, 9.10020e+00, 7.98270e+00, 7.49300e+00,
-3.28730e+00, 9.36000e-02, 3.46120e+00, 2.97870e+00,
1.67290e+00, 2.43910e+00, -2.80870e+00, -2.44900e+00,
-9.97900e-01, -1.97800e-01, -1.08000e-01, -2.63600e-01,
8.78000e-02, 4.40860e+00, -6.57400e-01, 8.15900e-01,
7.45070e+00, 7.13330e+00, 1.13950e+00, -2.55000e-02,
1.07700e+00, -2.95130e+00, 1.58060e+00]))
Plot the topographic surface and the gravity data
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(topo, color="grey")
p.add_mesh(
grav,
point_size=15,
render_points_as_spheres=True,
scalar_bar_args={"title": "Observed Gravtiy Data"},
)
# Use a non-phot-realistic shading technique to show topographic relief
p.enable_eye_dome_lighting()
p.show(window_size=[1024, 768])
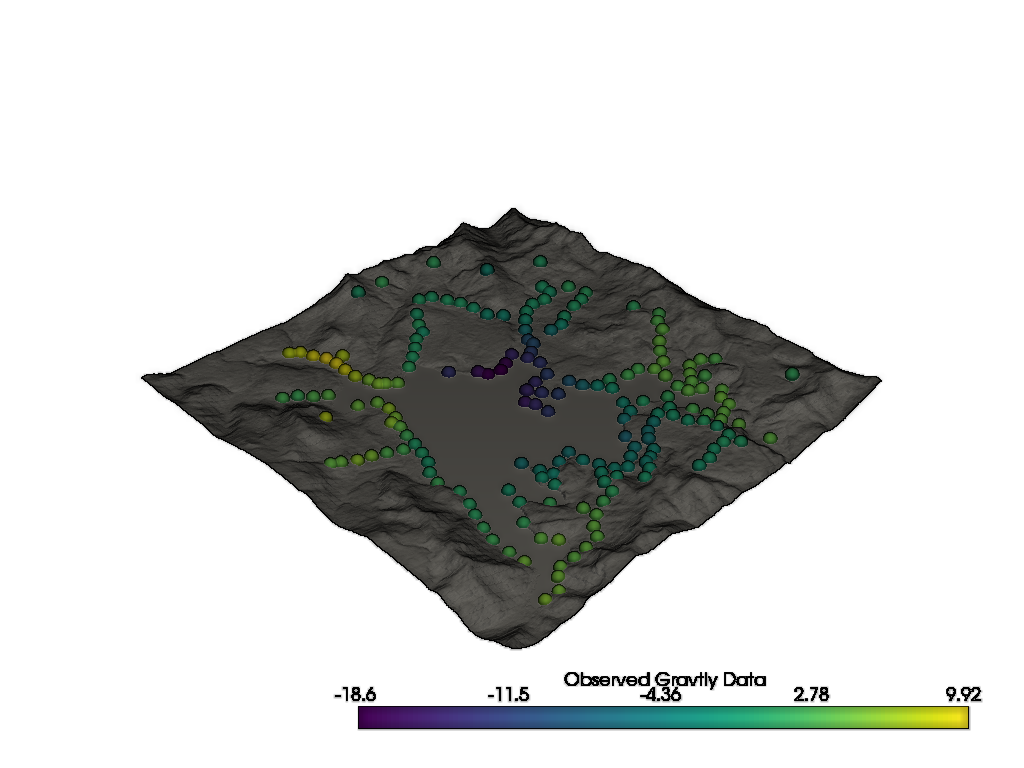
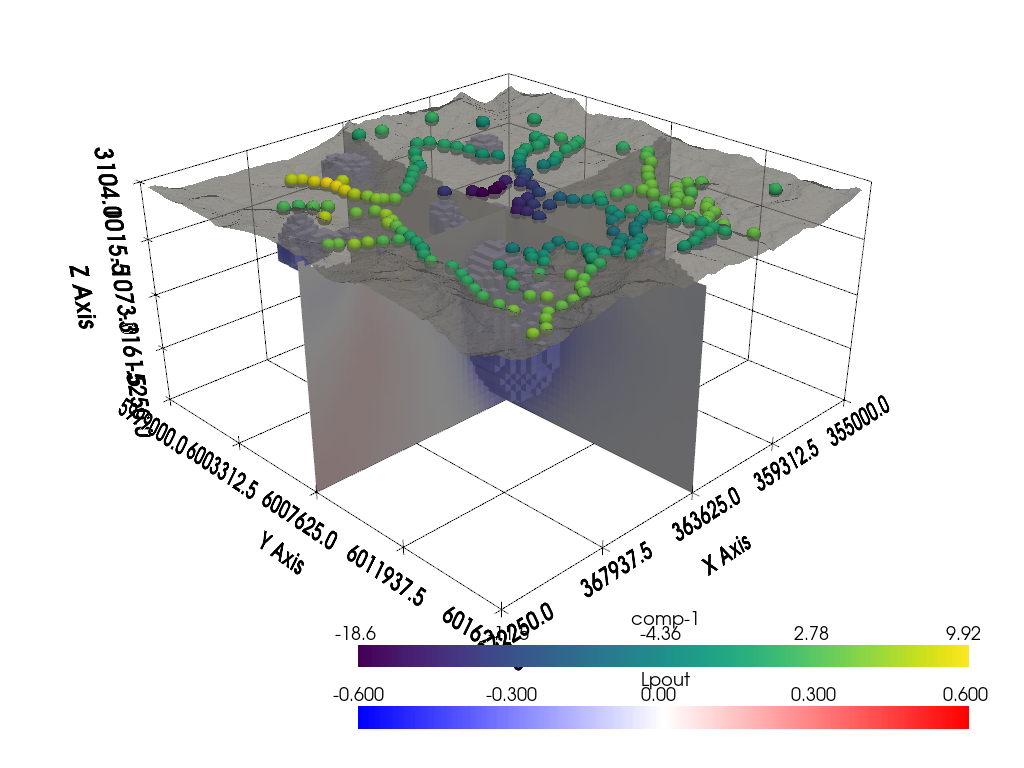
Visualize Using PyVista#
Here we visualize all the data in 3D!
# Create display parameters for inverted model
dparams = dict(
show_edges=False,
cmap="bwr",
clim=[-0.6, 0.6],
)
# Apply a threshold filter to remove topography
# no arguments will remove the NaN values
dataset_t = dataset.threshold()
# Extract volumetric threshold
threshed = dataset_t.threshold(-0.2, invert=True)
# Create the rendering scene
p = pv.Plotter()
# add a grid axes
p.show_grid()
# Add spatially referenced data to the scene
p.add_mesh(dataset_t.slice("x"), **dparams)
p.add_mesh(dataset_t.slice("y"), **dparams)
p.add_mesh(threshed, **dparams)
p.add_mesh(
topo,
opacity=0.75,
color="grey",
# cmap='gist_earth', clim=[1.7e+03, 3.104e+03],
)
p.add_mesh(grav, cmap="viridis", point_size=15, render_points_as_spheres=True)
# Here is a nice camera position we manually found:
cpos = [
(395020.7332989303, 6039949.0452080015, 20387.583125699253),
(364528.3152860675, 6008839.363092581, -3776.318305935185),
(-0.3423732500124074, -0.34364514928896667, 0.8744647328772646),
]
p.camera_position = cpos
# Render the scene!
p.show(window_size=[1024, 768])
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 20.552 seconds)
