Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Basic Forward 2D DC Resistivity#
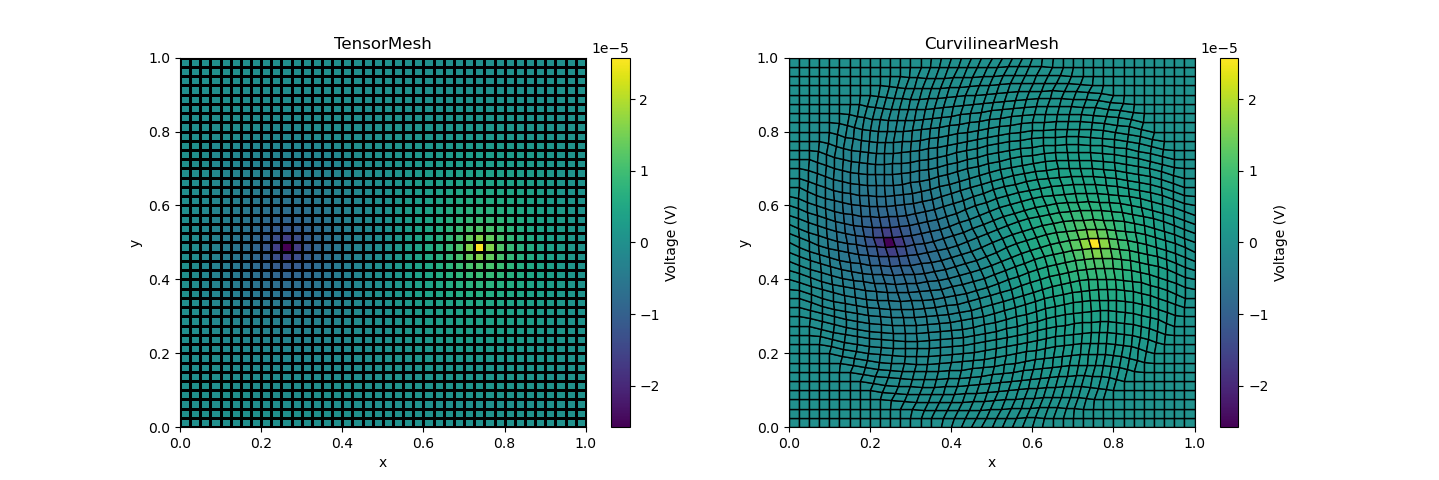
2D DC forward modeling example with Tensor and Curvilinear Meshes
/home/vsts/work/1/s/examples/plot_dc_resistivity.py:32: DeprecationWarning: The closest_points_index utilty function has been moved to be a method of a class object. Please access it as mesh.closest_points_index(). This will be removed in a future version of discretize
txind = discretize.utils.closest_points_index(mesh, pts)
import discretize
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.sparse.linalg import spsolve
def run(plotIt=True):
# Step1: Generate Tensor and Curvilinear Mesh
sz = [40, 40]
tM = discretize.TensorMesh(sz)
rM = discretize.CurvilinearMesh(
discretize.utils.example_curvilinear_grid(sz, "rotate")
)
# Step2: Direct Current (DC) operator
def DCfun(mesh, pts):
D = mesh.face_divergence
sigma = 1e-2 * np.ones(mesh.nC)
MsigI = mesh.get_face_inner_product(
sigma, invert_model=True, invert_matrix=True
)
A = -D * MsigI * D.T
A[-1, -1] /= mesh.cell_volumes[-1] # Remove null space
rhs = np.zeros(mesh.nC)
txind = discretize.utils.closest_points_index(mesh, pts)
rhs[txind] = np.r_[1, -1]
return A, rhs
pts = np.vstack((np.r_[0.25, 0.5], np.r_[0.75, 0.5]))
# Step3: Solve DC problem (LU solver)
AtM, rhstM = DCfun(tM, pts)
phitM = spsolve(AtM, rhstM)
ArM, rhsrM = DCfun(rM, pts)
phirM = spsolve(ArM, rhsrM)
if not plotIt:
return
# Step4: Making Figure
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12 * 1.2, 4 * 1.2))
vmin, vmax = phitM.min(), phitM.max()
dat = tM.plot_image(phitM, ax=axes[0], clim=(vmin, vmax), grid=True)
cb0 = plt.colorbar(dat[0], ax=axes[0])
cb0.set_label("Voltage (V)")
axes[0].set_title("TensorMesh")
dat = rM.plot_image(phirM, ax=axes[1], clim=(vmin, vmax), grid=True)
cb1 = plt.colorbar(dat[0], ax=axes[1])
cb1.set_label("Voltage (V)")
axes[1].set_title("CurvilinearMesh")
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.222 seconds)
