Operators#
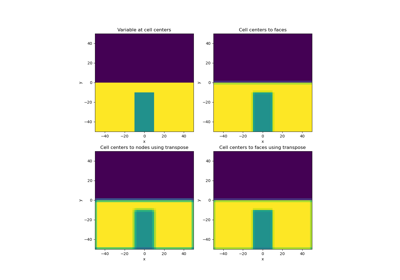
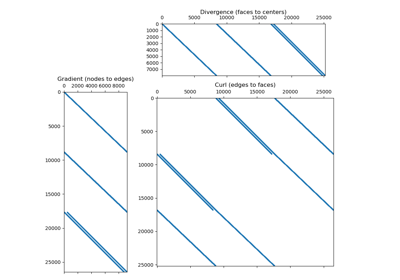
Numerical solutions to differential equations using the finite volume method require discrete operators. These include averaging operators and differential operators. Averaging operators are used when a variable living on some part of the mesh (e.g. nodes, centers, edges or faces) must be approximated at other locations. Differential operators include the gradient, divergence, curl and scalar Laplacian.
The discrete operators are properties of each mesh class (tensor mesh, tree mesh, curvilinear mesh). An operator is only constructed when called. Since each mesh type has a similar API, the operators can be called using the same syntax.
To learn about discrete operators, we have provided a set of tutorials. These tutorials aim to teach the user:
how to construct averaging and differential operators from a mesh
how to apply the discrete operators to discrete variables
how to impose boundary conditions using differential operators
how discrete differential operators preserve vector calculus identities